By TZ Business News Staff.
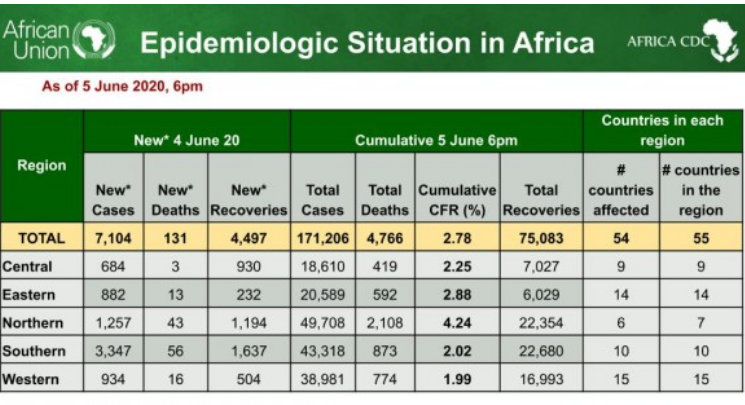
The Africa Centre for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) published data on Friday, June 5, 2020 which showed Tanzania’s Coronavirus recovery rate was lower than the continental African average by some 4 percentage points.
The data also showed Tanzania’s death rate was 1.1 percentage points higher than the African average.
At 18.00 Hours East African time on Friday, the data showed 54 African Union (AU) Member States had reported a total 171,206 COVID-19 cases, 4,766 deaths and 75,083 recoveries. Tanzania had reported 509 cases, 21 deaths and 178 recoveries.
Regional data showed Nothern Africa leading with 49,708 reported Covid-19 cases, followed by Southern African at 43,318 cases, then Western Africa with 38,981, followed by Eastern Africa with 20, 589 cases. Central Africa had the least number of reported Covid-19 cases at 18,610.
CDC has in the meantime announced a robust plan to contain the Covid-19 virus through increased testing and monitoring and unleashing an ‘army’ of one million health workers throughout the continent to trace the infected.
The AU Commissioner for Social Affairs, H.E. Mrs Amira Elfadil Mohammed, on Friday rolled out the Partnership to Accelerate COVID-19 Testing (PACT) at the African Union Commission headquarters in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia.
“Until today there is no treatment or vaccine for COVID-19. This leaves us with only prevention, and when it comes to prevention our choices are limited, she said. “We must prevent more transmission by doing more testing and tracing and this is what PACT is about. That is why we are supporting Member States to do more testing, to trace, and to identify and isolate infected persons.
“In this way we will be able to control the virus and limit transmission on the continent,” she said. “PACT is a vital component of the continental response to COVID-19 and it is the key to ensuring that we unlock our economies in a safe manner.”
In a message to participants at the rollout event in Addis, the Chairperson of the African Union Commission, H.E. Moussa Faki Mahamat, said: “We have set four goals for PACT: to scale up testing for COVID-19, to continue training healthcare workers on the continent, to establish a platform for pooled procurement at Africa CDC, and to deploy one million community workers who will help trace contacts of confirmed cases.
Anchored on the African Union Joint Continental Strategy for COVID-19 endorsed by Africa health ministers and the Bureau of Heads of State and Government of the African Union, PACT is an initiative to help prevent transmission and deaths, and minimize the social and economic harm due to COVID-19. It seeks to implement well-coordinated actions and strong partnerships to strengthen the effectiveness of response across Africa.
PACT has three key components: Test, Trace and Treat. Testing to diagnose cases, tracing to identify cases and their contacts, and treating to provide treatment and supportive care to cases.
“The intention of PACT is to focus on some specific aspects of the response that we must do very quickly. We want to test so we can find where the virus is hiding in the community. When we test, we expect to see more cases and we must trace the contacts and treat those who are infected, otherwise the testing will be of no value,” said Dr John Nkengasong, Director of Africa CDC.
With a population of about 1.2 billion, Africa has recorded more than 150,000 cases of COVID-19 and conducted just about 2.4 million tests. To achieve its testing goal of 8000 tests per million population, Africa needs to intensify testing to identify and isolate cases and trace their contacts, and this requires huge resources that cannot be mobilized without the strong partnerships that PACT will facilitate. “PACT is the game changer that will help capacitate Africa and enable it to build the strong partnerships needed to mobilize resources and support to defeat COVID-19 on the continent,” said Dr John Nkengasong.



